Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Loaded with Callistemon citrinus Phenolics Exhibited Anticancer Properties against Three Breast Cancer Cell Lines

Less harmful acidic degradation of poly(lacticco-glycolic acid) bone tissue engineering scaffolds through titania nanoparticle addition. - Abstract - Europe PMC
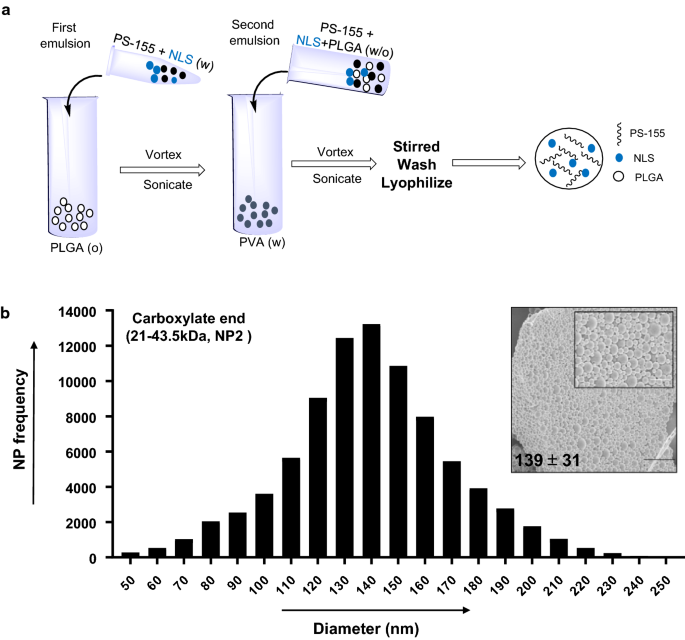
Investigation of PLGA nanoparticles in conjunction with nuclear localization sequence for enhanced delivery of antimiR phosphorothioates in cancer cells in vitro | SpringerLink
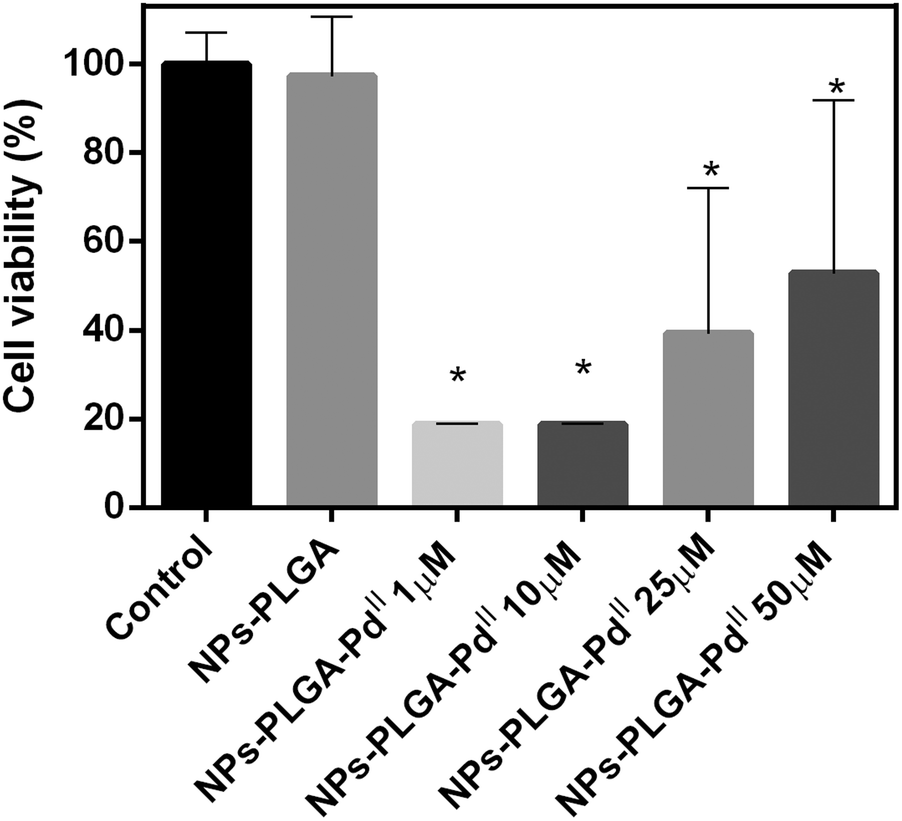
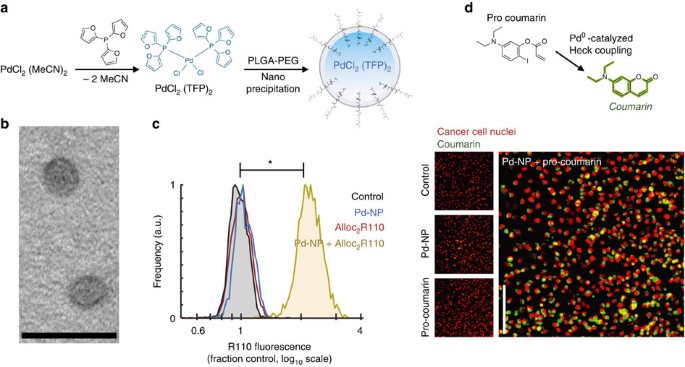
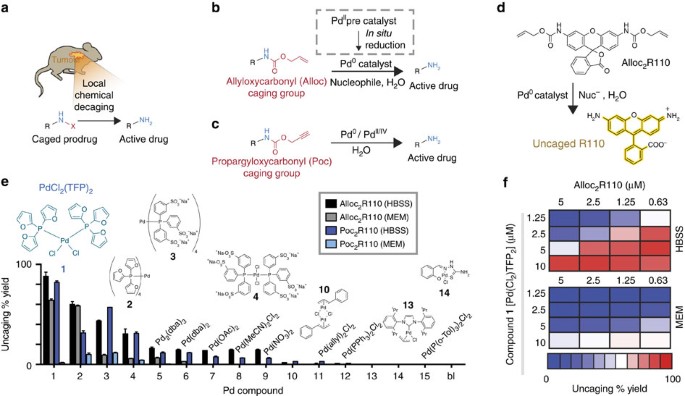
PLGA-nanoparticles loaded with a thiosemicarbazone derived palladium( ii ) complex as a potential agent to new formulations for human ovarian carcinom ... - New Journal of Chemistry (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D0NJ00580K
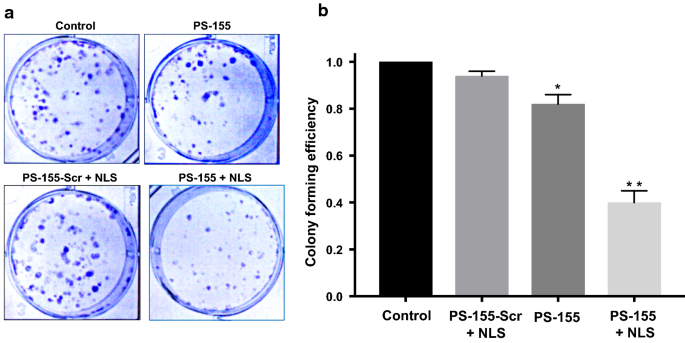
Investigation of PLGA nanoparticles in conjunction with nuclear localization sequence for enhanced delivery of antimiR phosphorothioates in cancer cells in vitro | SpringerLink

Poly(2‐propylacrylic acid)/poly(lactic‐co‐glycolic acid) blend microparticles as a targeted antigen delivery system to direct either CD4+ or CD8+ T cell activation - Yang - 2017 - Bioengineering & Translational Medicine - Wiley Online
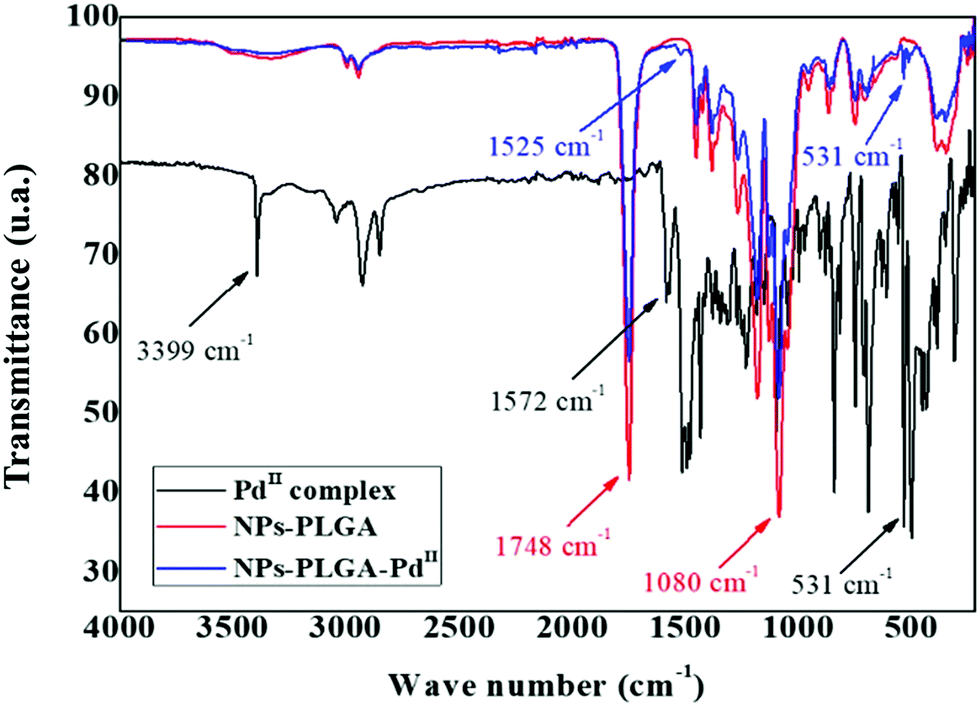
PLGA-nanoparticles loaded with a thiosemicarbazone derived palladium(ii) complex as a potential agent to new formulations for human ovarian carcinoma treatment - New Journal of Chemistry (RSC Publishing)

Bentham Science | Publisher of excellence for all Biomedical, Medical and Pharmaceutical Decision Makers

Figure 1 from Thymoquinone-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: antioxidant and anti-microbial properties | Semantic Scholar

Chitosan surface modified PLGA nanoparticles loaded with brigatinib for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer in: Journal of Polymer Engineering Volume 39 Issue 10 (2019)

Monomer sequence in PLGA microparticles: Effects on acidic microclimates and in vivo inflammatory response - ScienceDirect

Trimethoprim-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Grafted with WGA as Potential Intravesical Therapy of Urinary Tract Infections-Studies on Adhesion to SV-HUCs Under Varying Time, pH, and Drug-Loading Conditions. - ACS Omega - X-MOL
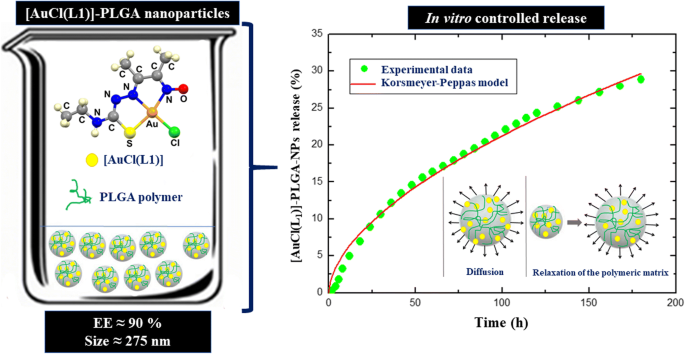
Development of gold(III) thiosemicarbazonate complex–loaded PLGA nanoparticles: characterization and sustained release studies | SpringerLink
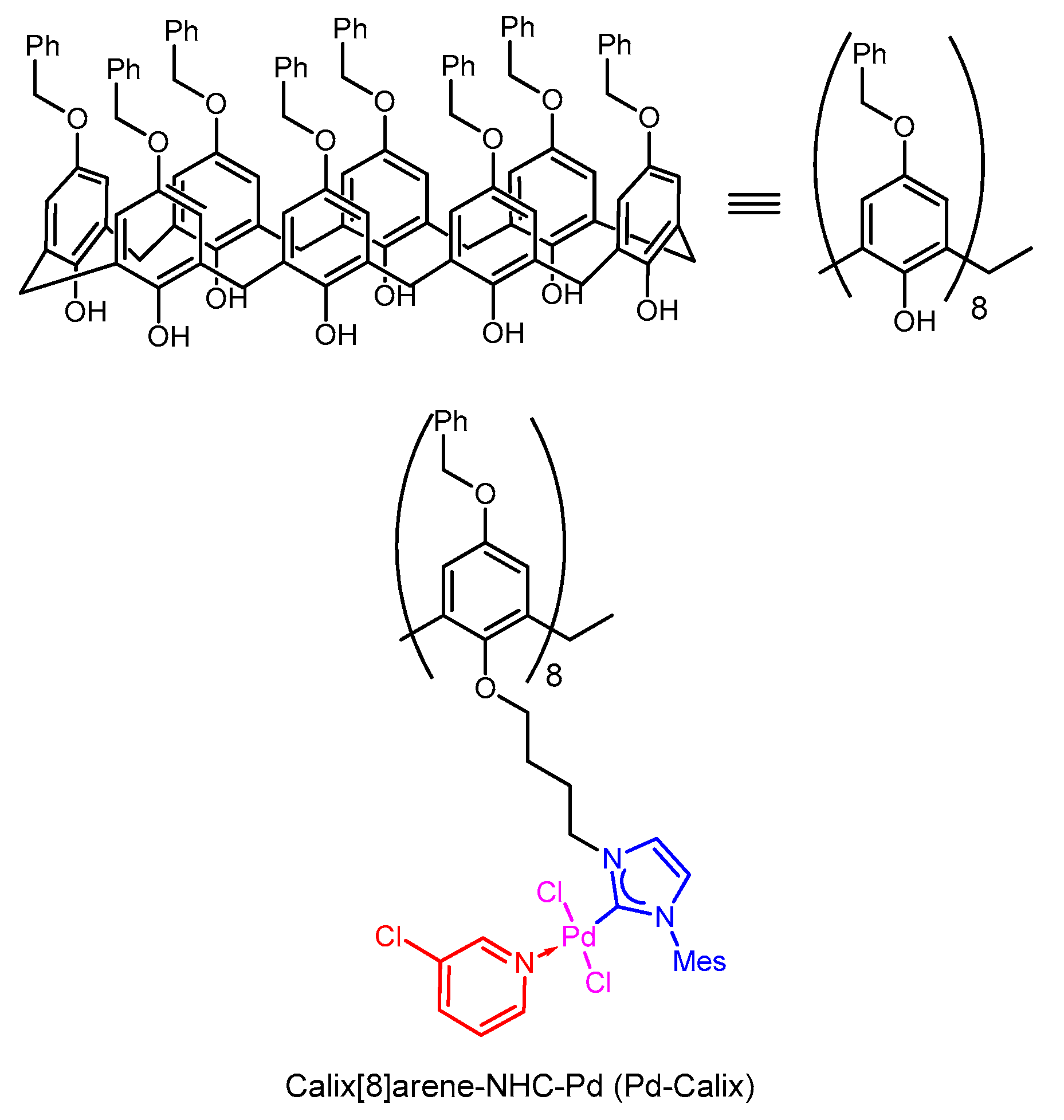
Molecules | Free Full-Text | A Self-Assembling NHC-Pd-Loaded Calixarene as a Potent Catalyst for the Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction in Water | HTML
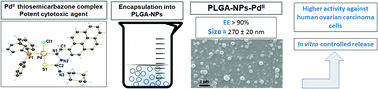
PLGA-nanoparticles loaded with a thiosemicarbazone derived palladium(ii) complex as a potential agent to new formulations for human ovarian carcinoma treatment - New Journal of Chemistry (RSC Publishing)

CD30 aptamer-functionalized PEG-PLGA nanoparticles for the superior delivery of doxorubicin to anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells - ScienceDirect

Synthesis and characterization of PTX-PLGA-Ms. (A) Schematic showing... | Download Scientific Diagram

Comparative whole corona fingerprinting and protein adsorption thermodynamics of PLGA and PCL nanoparticles in human serum - ScienceDirect
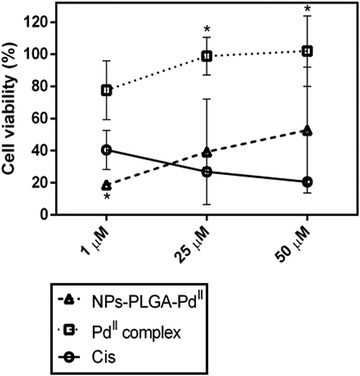
PLGA-nanoparticles loaded with a thiosemicarbazone derived palladium(ii) complex as a potential agent to new formulations for human ovarian carcinoma treatment - New Journal of Chemistry (RSC Publishing)